Support Page Content
Addressing Islamophobia
What is Islamophobia?
Islamophobia, in general, is fear, hostility or hatred directed at Islam, Muslims, those perceived as Muslims, and allies of Muslims. Islamophobia is rooted in prejudice and racism and manifests itself systematically and unfairly through discriminatory, exclusionary, oppressive, dehumanizing and violent practices. Combating Islamophobia on campus is urgent because of its harmful and corrosive consequences for our community.
You can learn more about Islamophobia by visiting the following webpages.
| Resource Name | Link |
|---|---|
| The Bridge Initiative: Georgetown University | What is Islamophobia? |
| Islamophobia Studies Center | Defining Islamophobia |
What do I do if I experience or witness Islamophobia on campus?
If you experience or witness acts of Islamophobia on campus, there are ways to report them and get support.
Belonging Support Form
Submit this form to get support from Inclusive Excellence.
Office for Equal Opportunity Reporting Tool
The Office for Equal Opportunity works to investigate allegation of discrimination, harassment and retaliation based on protected class categories: race/ethnicity, gender and gender expression, age, national origin, disability, religion, of which, ancestral and ethnic group are included.
Office for Equal Opportunity Reporting Tool
How are we addressing Islamophobia at Sacramento State?
At Sacramento State, we are committed to addressing Islamophobia through proactive education, advocacy, and community engagement.
Islamophobia Advisory Council
Our Islamophobia Advisory Council plays a vital role in this initiative by bringing together students, faculty, and community members to identify challenges and develop strategies that foster understanding and respect for Muslim identities. The council focuses on raising awareness about Islamophobia, promoting inclusivity, and creating a safe environment for all. Through workshops, training sessions, and collaborative events, we aim to combat stereotypes, encourage dialogue, and support our diverse Muslim community, ensuring that every individual feels valued and respected on campus.
What are the origins of Islamophobia?
Islamophobia has deep historical roots shaped by various factors over time:
Medieval Conflicts: During the Crusades, Christian Europe demonized Muslims, portraying them as barbaric and morally inferior, creating a long-lasting narrative of Muslims as the "other."
Colonialism and Orientalism: European imperialism reinforced negative stereotypes of Muslims as backward and culturally inferior. Edward Said's concept of Orientalism highlights how Western media depicted the Muslim world as exotic and dangerous.
Migration and Nationalism: Post-colonial migration to the West led to tensions around identity and integration, fueling Islamophobia driven by cultural anxieties.
Geopolitical Conflicts: Ongoing conflicts involving Muslim-majority nations, like the Gulf Wars and Israeli-Palestinian tensions, contributed to the framing of Islam as inherently violent.
9/11 and Terrorism: After the 9/11 attacks, Islam became associated with terrorism, leading to a surge in Islamophobia, particularly in the U.S. and Europe.
Media and Political Rhetoric: Negative media portrayals and political rhetoric, especially from far-right groups, have reinforced harmful stereotypes of Muslims.
Understanding these origins is crucial to effectively challenging Islamophobia today.
What is Islam?
Islam is one of the world's major monotheistic religions, with over 1.9 billion followers, known as Muslims. Centered on the belief in one God (Allah) and the teachings of the Prophet Muhammad, who is considered the last prophet, Islam emphasizes submission to God's will as the path to spiritual fulfillment. The faith is structured around the Five Pillars of Islam: the declaration of faith (Shahada), five daily prayers (Salat), giving to charity (Zakat), fasting during Ramadan (Sawm), and the pilgrimage to Mecca (Hajj). The Qur'an, believed to be the literal word of God as revealed to the Prophet Muhammad, serves as the holy scripture guiding Muslim beliefs and practices.
Unlike some other religions, Islam does not have a central authority (like the Vatican for Catholicism). Instead, various scholars and leaders interpret Islamic teachings and practices within diverse cultural contexts. This decentralized structure allows for a variety of interpretations and practices among different Muslim communities. Sharia law, derived from the Qur'an and Hadith (sayings of the Prophet Muhammad), encompasses a broad range of civil, criminal, and ethical guidelines that govern the lives of Muslims. While Sharia is often misunderstood and misrepresented, it primarily emphasizes justice, compassion, and the welfare of the community. Islam teaches the importance of community (Ummah), the oneness of God (Tawhid), and accountability in the afterlife (Akhira). While the two main branches of Islam—Sunni and Shia—differ in leadership interpretations, they share core values like compassion, justice, and the pursuit of knowledge. Overall, Islam encourages ethical living and harmonious relationships among all people.
| Resource | Link |
|---|---|
| Islamophobia Education Collective | Resources to Learn About Islam |
Who are Muslims?
Muslims are a diverse group of individuals who come from various cultural, ethnic, and national backgrounds, demonstrating that Islam is a truly global faith. While many people associate Muslims with the Middle East, the reality is that the majority of Muslims live in regions such as South Asia, Southeast Asia, and Africa, with significant communities in Europe, North America, and beyond. Furthermore, Muslims are not exclusively of Arab descent; they encompass a wide array of ethnicities, including but not limited to South Asians, Indonesians, Africans, and Europeans. Additionally, Islam has attracted many converts from different walks of life, further enriching the Muslim community with varied perspectives and experiences.
Unfortunately, the racialization of Muslims often leads to stereotypes and misconceptions that fail to recognize this diversity, framing them solely through the lens of ethnicity or culture rather than their shared faith. This racialization frequently manifests in the portrayal of Muslims in media and political discourse, where they are often homogenized and depicted as a monolithic group, reinforcing harmful stereotypes associated with terrorism or extremism. Such narratives can marginalize the voices and experiences of Muslims from different backgrounds, leading to social stigmatization and discrimination. Moreover, racial profiling and Islamophobia can exacerbate feelings of alienation among Muslim communities, making it essential to highlight their rich diversity and challenge the reductive views that fuel prejudice. This complexity reflects the universal message of Islam, which transcends geographical and cultural boundaries, emphasizing unity in faith while celebrating individual identities.
The following maps show the global Muslim population as of 2009.
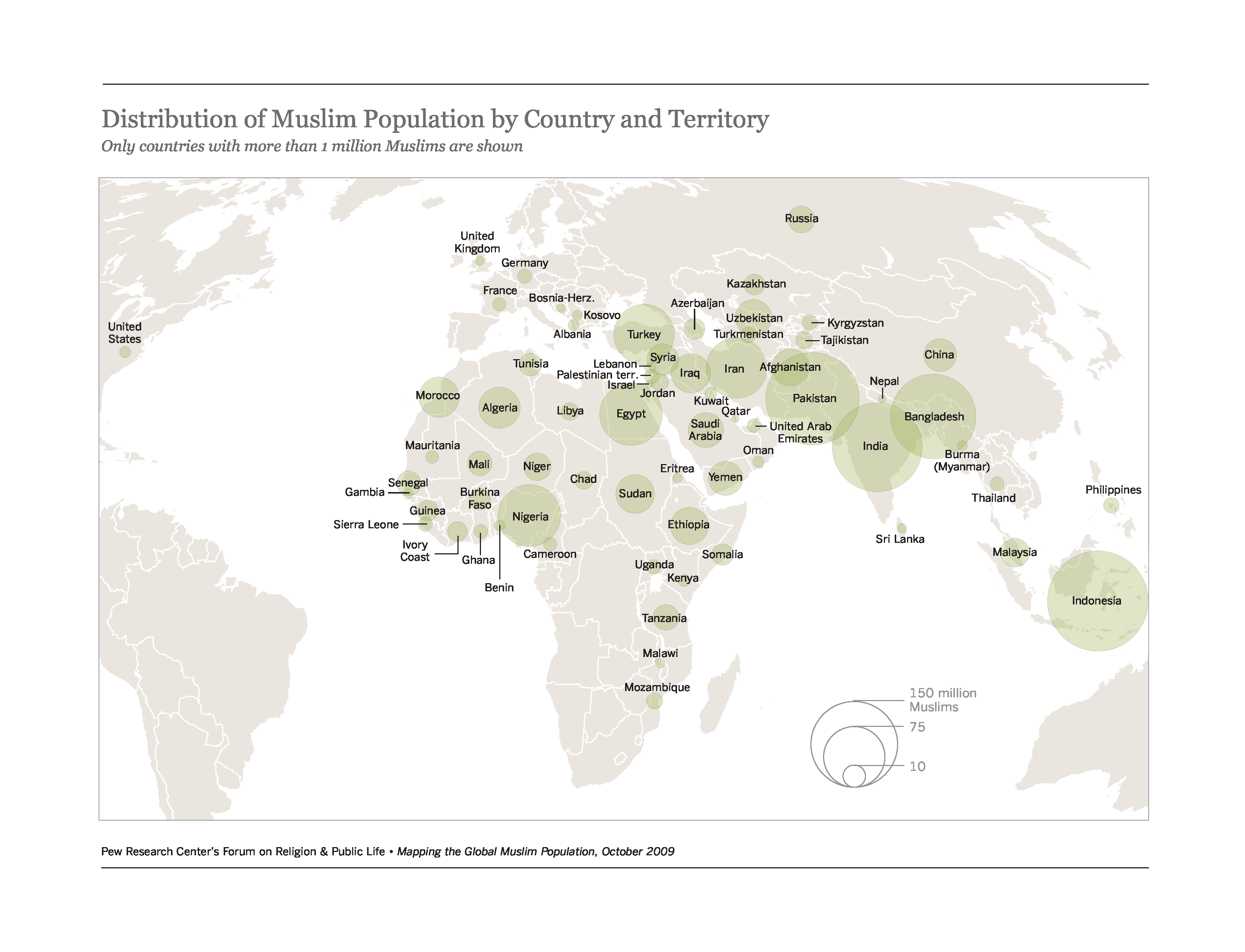
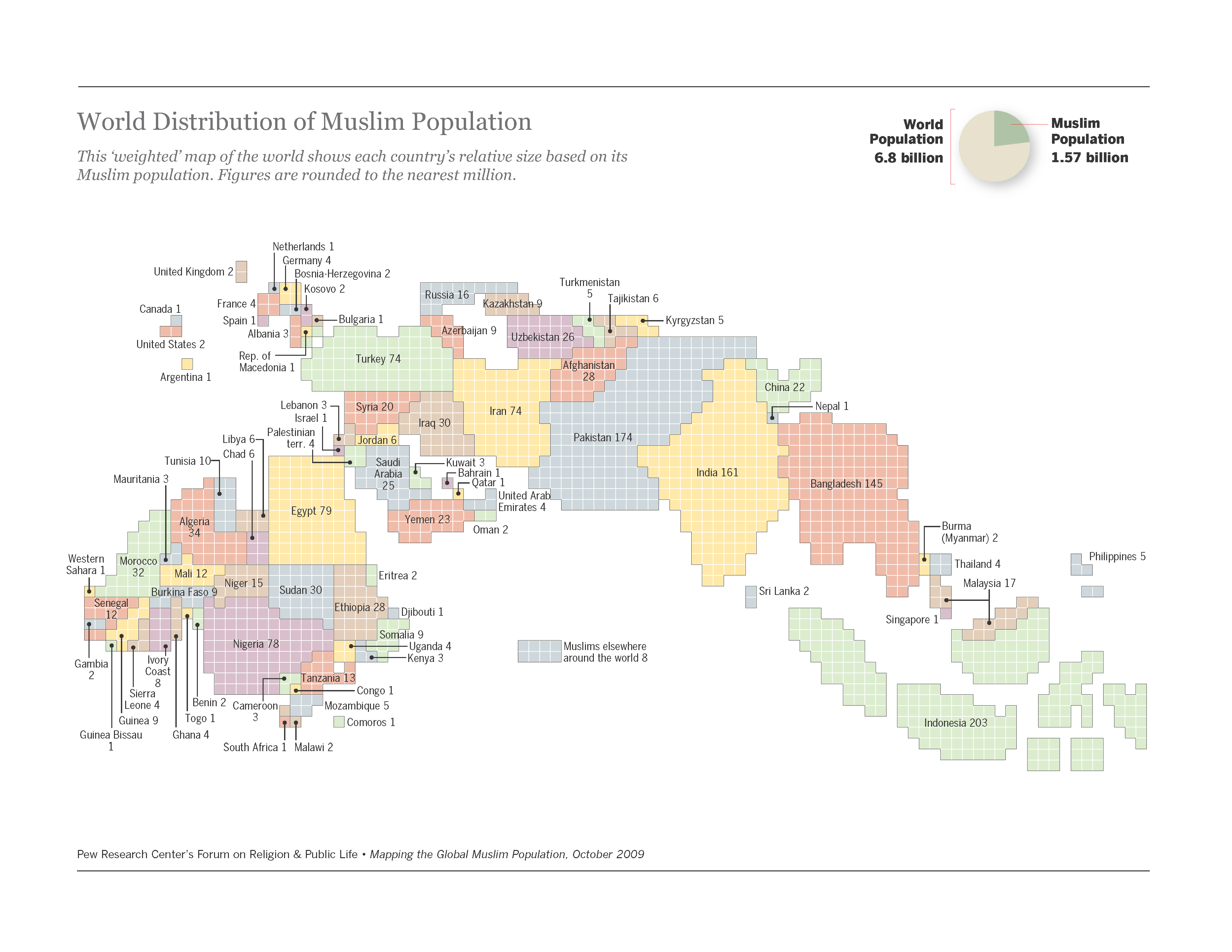
| Resource Name | Link |
|---|---|
| 25 Influential American Muslims Video | Youtube Video |
| Article: Muslim Victimization in the Contemporary US by Sarah Beth Kaufman and Hanna Niner | Article Link |
| Mapping the Global Mulsim Population: A Report from Pew Research | Report Link |
How does Islamophobia affect our campus community?
Islamophobia can significantly impact our campus community by fostering an environment of fear, exclusion, and misunderstanding. Muslim students may experience discrimination, harassment, or microaggressions, leading to feelings of isolation and anxiety, which can adversely affect their mental health and academic performance. The stress and trauma associated with Islamophobia can result in increased rates of anxiety, depression, and other mental health challenges among affected individuals. This climate of fear can deter individuals from expressing their beliefs or engaging in campus activities, undermining the principles of diversity and inclusion. Additionally, Islamophobia can create divisions among different cultural and religious groups, hindering the collaborative spirit essential for a vibrant academic community. By addressing Islamophobia, we aim to promote a culture of respect, understanding, and solidarity, ensuring that all students feel safe, supported, and empowered in their identities.
| Resource | Link |
|---|---|
| Institute for Social Policy and Understanding | Mental Health Toolkit - ISPU |
| Maristan | Maristan Mental Health Clinic |
Additional Resources
Below is a list of additional resources about Islams, Muslims, and Islamophobia. For more information, pelase contact Inclusive Excellence at diversity@csus.edu.