Language and Speech Perception
Speech Perception:
examined at multiple levels of analysis.
(phonemes, words, sentences, text/story).
Problems arise at each level
1) Phonemes-
e.g. "a" is different in "baby" and "back"
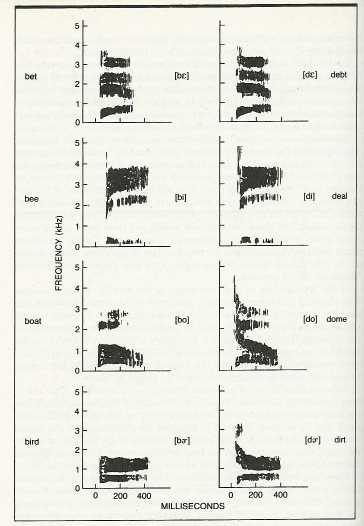
Problem of Invariance:
1.
e.g.
2.
coarticulation -


Result of coarticulation:
Solutions to Problem of Invariance:
solution 1.
linguistic info: background to Liberman experiment
pronunciation of "b" and "p" done in a similar way.
only difference -
b:
p:
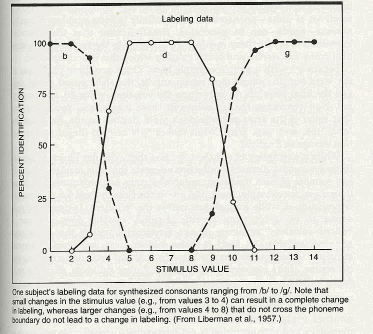
Experiment by Liberman, et. al (1957)
method:
Results:
•
•
solution 2:
experiment by Warren & Warren (1970)
method:
•
•
e.g. It was found that the *eel was on the orange.
It was found that the *eel was on the shoe.
Result:
1.
2.
3.
Experiment by Pollack and Pickett (1964)
Method:
Results:
solution 3:
McGurk Effect- found by McGurk and MacDonald, 1976
method:
Results:
Speech Perception: Next Level of Analysis:
Words: how do we perceive words?
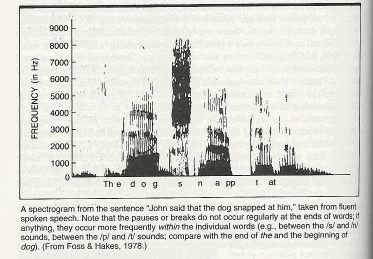
Problem:
So, how do we perceive words?
Theory of a Mental Lexicon:
lexicon contains:
a) pronunciation:
b) spelling:
c) part of speech:
d) meaning pointer -->
Experiments to investigate existence of a lexicon:
Experiment 1:
method of Cross-model priming:
Task:
Priming:
e.g.
Results:
Conclusion:
Experiment 2: Marslen-Wilson , et. al. (1989)
Method:
Results:
follow-up exp by Gaskell & Marslen-Wilson (1996)
method:
Condition A:
Condition B:
Results: