The
Visual System:
Neuron to Higher Level Processing

I. The Visual System: - 3 major areas
Eye
Lateral Geniculate nucleus (in the thalamus)
Visual Cortex - (a.k.a. striate cortex)
II. Light -
What is light? -- one kind of electromagnetic radiation
Light is both a particle and a wavelength.
Photon -
travel at a constant speed of about 300,000 km per second (speed of light).
the element that is absorbed by the photoreceptors in our eyes.
Wavelength -
Light:
from 400-700 nm (nanometers--1 billionth of a meter)
Other animals can perceive longer and shorter wavelengths
Light is structured by the environment
Ganzfeld-
III. Light Reception-
Types-
Light Gathering -
e.g. single-celled amoeba --
e.g. light sensitive area on lower forms of life-
Image-forming -
pinhole eye of Nautilus (mollusk) -
compound eye (insects) -
Vertebrate Eye -
IV. Anatomy of Human Eye -
From the outside (look in a mirror)
Sclera:
Pupil:
Iris:
Cornea:
On the Inside:
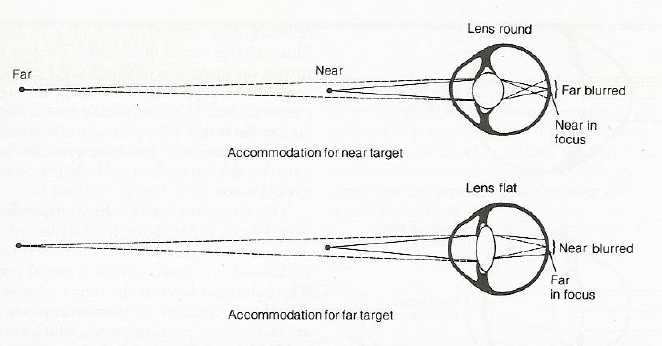
Lens:
accommodation:
for far away objects--
for nearby objects--
Retina:
Photoreceptors absorb light rays and transform them into information transmitted by the neurons to the brain.
Process:
photopigments: 2 components
1)
2)
Types of visual receptors
Rods:
Cones:
Fovea:
Perpiheral Retina -
Optic Nerve:
Location of the blind spot
V. Duplicity Theory -
Shape and Distruibution differences:
cones:
rods:
Dark Adaptation Differences -
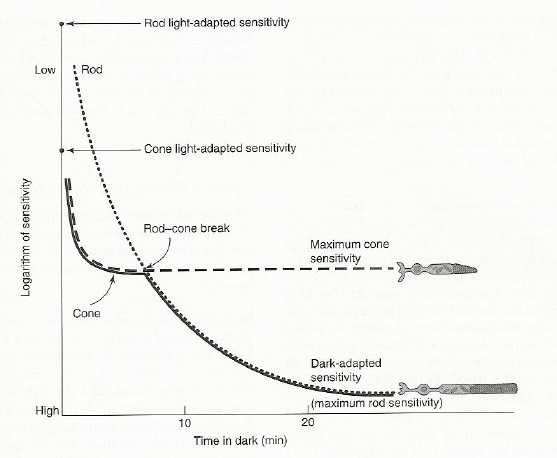
kink in the graph is due to the difference in rods and cones.
cones:
rods:
Light Adaptation Differences -
Spectral sensitivity (to different wavelengths along the spectrum), and color vision differences
cones: (Phototopic)-
cones:
rods: (Scotopic)-
rods:
Purkinje Shift -
Acuity -
cones:
rods:
Why the difference?
Convergence:
Results:
1)
2)
Measuring acuity:
VI. Vertical Connections in Retina:
Types of cells:
Bipolar:
midget bipolar cells --
Diffuse bipolar cells --
Ganglion cells:
How do this?
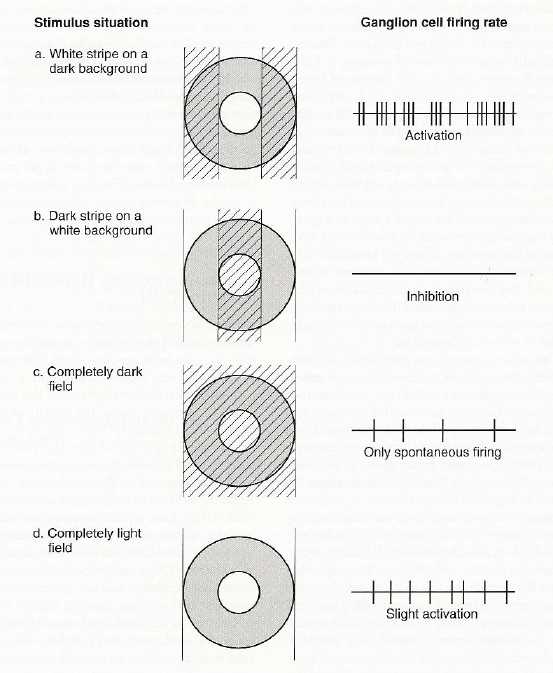
use single cell recording technique for one ganglion cell--find area on retina that corresponds to that one ganglion.
record normal low-level spontaneous level of activity of ganglion
then turn on light in & around that area and see how it effects the firing of the ganglion cell
ganglion cells respond differently depending on what area of their receptive field is stimulated
Two types of ganglion cells:
1) on-center, off-surround
2) off-center, on surround
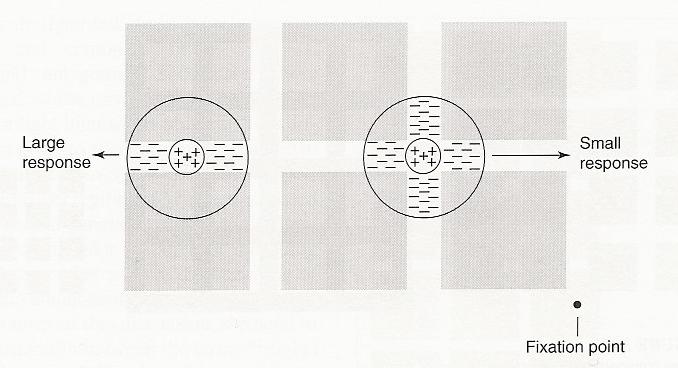
e.g. on-center, off-surround
How does this type of receptive field work?
Horizontal and Amacrine Cells:
Lateral Inhibition:
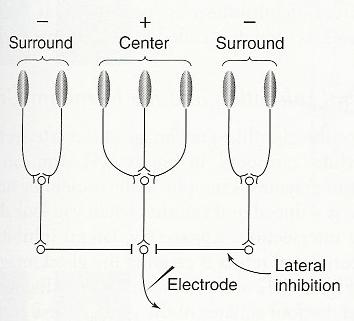
Mach Bands -
Explanation:
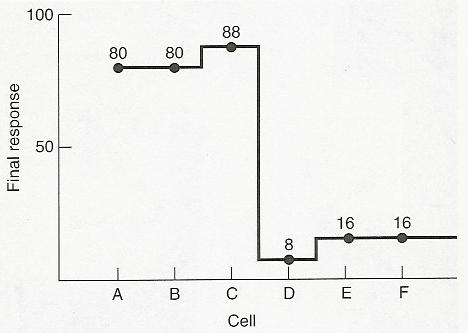
Also explains Hermann Grid & Scintillating Grid
Different amount of lateral inhibition cause the intersections to appear darker (dimmer) than the hallway areas.