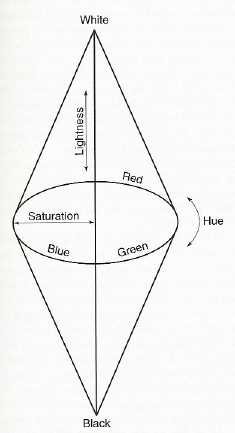
Hue:
Brightness:
Saturation:
Color Perception
Dimensions of Color:
Hue:
Brightness:
Saturation:
Color Mixture:
Subtractive Color Mixture:
e.g.
Additive Color Mixture:
complementary hues:
Trichromatic Theory of Color Vision: (Young-Helmholtz theory)
S-Cones:
M-Cones:
L-Cones:
e.g. a 450 nm light
e.g.
Color Blindness:
e.g.
protanopia -
deuteranopia -
Tritanopia -
Trichromatic Theory can't explain all color phenomenon though
Opponent-Process Theory:
3 types
Red-Green:
Yellow-Blue:
Black-White:
lateral inhibition creates the opponent process cells
Color Constancy:
Depth Perception:
absolute distance:
relative distance:
1. Monocular depth cues:
a. Linear Perspective
b. texture gradient
c. aerial perspective:
d. shadow/shading:
e. interposition (a.k.a. occlusion):
f. motion parallax

g. accretion and deletion

2. Binocular depth cues:
a. Stereopsis (a.k.a. binocular disparity):
e.g. stereograms & autostereograms
Oculomotor Depth Cues:
a.convergence:
b. accommodation:
3. Perception via Self Motion:
a. Optic Flow: