Learning
Learning:
e.g. learning to drive
e.g. learning to read
Learning Processes:
- Observational Learning:
e.g.
- Associative Learning:
e.g.
- Conditioning:
2 types of conditioning:
1. Classical Conditioning:
e.g.
2. Operant Conditioning:
e.g. children likely to repeat good manners if their parents reward them with praise or candy
Classical Conditioning (Pavlovian Conditioning): (Ivan Pavlov)
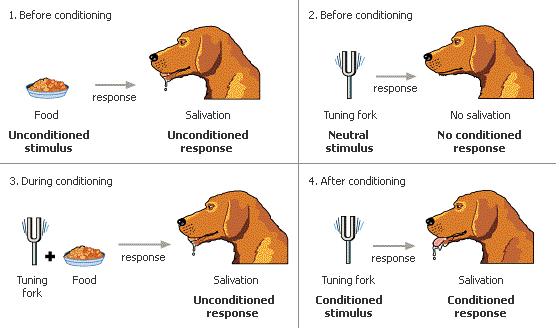
Pavlov: worked with digestive system in dogs and routinely put meat powder (food) in their mouths. He noticed that food normally elicited a salivation response. After a while he found that just the sight of the person that fed the dogs, the sound of the door opening, the sight of the food bowl elicited salivation in the dogs. He determined that the dogs had formed an association between these sights & sounds and the food.
e.g.
e.g.
e.g. pair the sound of the door with getting food many many times and eventually the dog hears the door and starts to salivate.
e.g.
Pavlov's Classic Experiment:

- Pavlov rang a bell --
- When given meat powder, dogs naturally salivate.
- Later he would always ring a bell immediately before giving meat powder to the dogs. (pairing the bell with presentation of meat powder).
- After some pairings, just ringing a bell alone with no food present would cause the dogs to salivate.
Other examples of classical conditioning:
- You hear a tone and then you get a puff of air to your eyes. After a few repetitions, hearing the tone makes you blink your eyes.
- Your alarm clock makes a faint clicking sound a couple of seconds before the alarm goes off. At first the click by itself does not awaken you, but the alarm does. After a week or so, however, you awaken as soon as you hear the click.
Phenomena of Classical Conditioning:
e.g. "Little Albert" study by John B. Watson.
Before Conditioning:
- White Rat (neutral stimulus) --> no response
- Loud Noise (UCS) --> fear & crying (UCR)
During Conditioning:
- paired loud noise with showing the white rat
After Conditioning:
- White Rat (CS) --> fear & crying (CR)
e.g.
Extinction:
e.g. Pavlov's dogs: if you ring the bell (CS) without presenting food (UCS) to the dogs many times in a row, then the dogs will eventually stop salivating to the bell ringing.
Spontaneous Recovery:
e.g. Pavlov's Dogs: after conditioning dogs to salivate to a bell, and then extinguishing that response. Then wait for a longer period of time (hours or days). If ring a bell again, will see at least some salivation. (spontaneous recovery).
e.g. if bell paired with food then the dogs will salivate
if the bell is not paired with food the dogs stop salivating after a while.
then wait for a few hours or days
after the delay there is no obvious current condition so when ring the bell again, some salivation will occur.

Applications of Classical Conditioning:
Phobias:
e.g. Little Albert had a fear of white furry things based on conditioning (pairing white rat with loud banging noise)
e.g.
can use conditioning to eliminate phobias
counterconditioning:
e.g. Peter -- baby with same fears as Little Albert although not induced in lab
brought in a white rat that he was afraid of and placed it far away (so not as fearful)
at the same time fed him cookies and milk (pleasurable)
each day brought rat a little closer while feeding him cookies and milk
Eventually Peter ate while petting the rat (was not scared of the rat)
Drug Dependence:
smoking can become a conditioned response to various environmental stimuli
e.g.
tolerance build up to drugs can depend partly on classical conditioning
tolerance: users of certain drogs experience progressively weaker effects after taking the drugs repeatedly. So, users crave larger amounts of the drug.
e.g. effect of classical conditioning.
when injecting a drug such as morphine or heroin, the stimuli during the procedure can become conditioned stimuli (time, place, etc.)
Before conditioning:
stimuli in room are neutral --> no response
drug enters brain (UCS) --> body's defense started against drug (UCR)
During Conditioning:
After Conditioning:
stimuli in room (CS) --> body's defense started against drug (CR)
example:
rats given alcohol in a cage with flashing lights and loud sounds
over time they get better and better at maintaining their balance when given the same amount of alcohol
then turn off flashing lights and sounds and give them the same amount of alcohol
Results:
Taste Aversions:
conditioned taste aversion:
e.g. laboratory rats drink a novel flavor liquid and then are made sick later by some illness-inducing drug.
can be used to help prevent loss of appetite for people undergoing chemotherapy (induces nausia).
Advertising: use classical conditioning in ads
e.g.
Beautiful woman (UCS) --> emotional arousal (UCR) in males
Beautiful woman (UCS) paired with an automobile many times
Automobile (CS) --> emotional arousal (CR) in males