Orbits:
Consider a spacecraft at point, P:
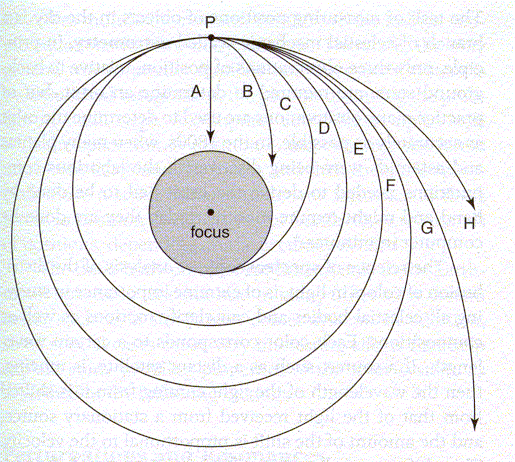
- If a rocket is not fired, it will fall to the ground on
path A
- A short burst results in
an elliptical orbit, intersecting Earth, along path B
- A higher speed almost
allows the spacecraft to avoid colliding with Earth (path C)
- A higher speed still
results in a complete elliptical orbit (path D)
- A circular velocity results in a circular orbit (path E)
- Higher speeds result in
additional elliptical orbits (path F)
- The
escape velocity results in a parabolic orbit (path G)
- Speeds
greater than the escape velocity result in hyperbolic orbits (path H)

|
|