1. What
type of aquifer lies beneath the
A. Confined
B. Fractured
crystalline
C.
Unconfined
D. Coastal
E.
None of the above
2. Most
of the groundwater in the
A.
Detrital sediment and
sedimentary rock.
B. Cyrstalline rock.
C. Rivers and streams.
D. Underground rivers.
3. Artesian
wells are most often associated with ________________ aquifers.
A. Deep
B. Mountain
C. Unconfined
D. High
permeability
E. Confined
4. A
rock or sediment that is capable of storing a large volume of water would have
which of the following properties?
A. Large
hydraulic conductivity.
B. High
permeability.
C.
High
porosity.
D. Crystalline
pore structure.
E.
None of the above, because the ability of a rock or
sediment to store water is determined primarily by the mineralogy of the
material.
5. Recharge,
or water entering aquifers, comes mostly from ______________.
A. Dehydration
of minerals.
B. Volcanic
degassing (also called “out-gassing”).
C. Seepage
from oceans.
D. Seepage
from lakes.
E. Precipitation.
6. When
a rock or other solid is permanently deformed by stress, it is said to deform
by ___________.
A. Plastic
failure
B. Brittle
failure
C. Elastic
rebound
D.
Plastic
strain
E.
Total strain
7. Which
of the following is not a factor contributing to the way a rock strains?
A. How
fast stress is applied.
B. The
composition of the material.
C. The
temperature of the rock.
D.
The age of
the rock.
E.
The depth of the rock in Earth’s crust.
8. Arrange
the following seismic waves in the order that they arrive at a seismograph
after an earthquake.
A. P-wave,
Surface wave, S-wave
B. S-wave,
Surface wave, P-wave
C. S-wave,
P-wave, Surface wave
D.
P-wave,
S-wave, Surface wave
E.
Can not be determined; wave speed depends on the type
of earthquake.
9. Which
of the following is the best definition of earthquake epicenter?
A. The
location along the fault where displacement occurred.
B. The
location that had the most ground motion.
C.
The location
on the earth’s surface directly above the focus.
D. The
location of the nearest seismograph.
E.
The emergency shelter set up after the earthquake.
10. Stress is to strain as ________
A. power is to energy.
B. law is to crime.
C.
cause is to effect.
D. a fold is to a fault.
E. Wilma is to Fred.
11. Imagine that two rocks with identical composition were subjected to the same stress, but one broke and the other bent. What probably accounted for the difference in the rocks’ response to stress?
A. They were stressed at different times.
B.
They were
stressed at different temperatures.
C. They were different ages.
D. Both B and C, above.
E. The question does not make sense because two rocks with identical composition will always respond the stress the in same way.
12. A seismograph records _________________
A. The buildup of strain energy prior to an earthquake.
B.
The movement
of the ground resulting from P-waves, S-waves and surface waves moving past the
seismograph.
C. The movement of the ground resulting from P-waves and S-waves moving past the seismograph; surface waves cannot be recorded by seismographs.
D. The location of an earthquake.
13. “The present is the key to the past” is a
statement of what geologic principle?
A. Catastrophism
B. Superposition
C. Inclusions
D.
Uniformitarianism
E.
Cross-cutting relationships
14. Arrange
these geologic eras in their proper sequence from youngest to oldest:
A. Mesozoic,
Precambrian, Cenozoic, Paleozoic.
B. Cenozoic,
Mesozoic, Paleozoic, Precambrian.
C.
Precambrian,
Paleozoic, Mesozoic, Cenozoic.
D. Paleozoic,
Mesozoic, Cenozoic, Precambrian.
E.
Precambrian, Paleozoic, Cenozoic, Mesozoic.
15. The
scientifically accepted age of the earth is___________.
A. 460
million years
B. 4.6
million years
C.
4.6 billion
years
D. 4.6
trillion years
E.
4.6 Gazillion-billion-million years
16. The most
important factor(s) that contribute(s) to the preservation of an organism as a
fossil are ___________.
A. The
organism has hard parts such as bones or a shell.
B. The
organism is quickly buried.
C. The
organism is from a species that is widespread.
D. All
of the above.
E. Both A and B.
17. Humans
first appear in which of the following geologic eras?
A. Mesozoic.
B. Palezoic.
C.
Cenozoic.
D. Humanozoic.
E.
Precambrian.
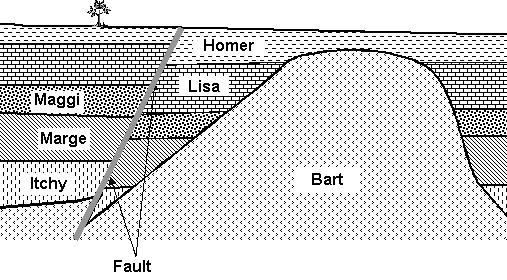
Refer to Figure 1 when answering questions 21 through 23.
Figure 1. A cross section of several
geologic units. The unit labeled
“Bart” is an igneous intrusion. All
other units are sedimentary rocks.
18. Which of the following statements is true about the geologic cross-section in Figure 1?
A.
Itchy is
older than Marge.
B. Homer is older than Itchy.
C. Bart an unconformity.
D. All of the above are true.
E. None of the above is true.
19. In the geologic cross-section shown in Figure 1 did faulting occur before or after the igneous intrusion Bart?
A. Before
B.
After
C. Not enough information is given
20. In the geologic cross-section shown in Figure 1 we know that Bart is younger than Lisa by
A. The principle of superposition
B. The law of inclusions
C. Absolute age dating
D.
Cross-cutting
relationships
E. The mother-son relationship (don’t use this answer!)
21. A mineral
contains a radioactive element called “Hornetonium,”
which has a half-life of 10,000 years. At the time the mineral
crystallized, there were 1,000,000 atoms of Hornetonium
in the mineral. Today the same mineral
contains are 250,000 atoms of Hornetonium. How long ago did the mineral crystallize?
A. 5,000
years
B. 10,000
years
C.
20,000 years
D. 40,000
years
E.
The age of the mineral can not be determined from the
information given.
22.
A. Volcanic
neck.
B. A
composite volcano.
C. Basaltic
lava flow.
D. A
geyser.
E. A collapsed caldera.
23. The most
important factor in determining magma viscosity is ________.
A. Temperature.
B. Dissolved
gasses.
C.
Silica
content.
D. The
color of the magma.
E.
None of the above.
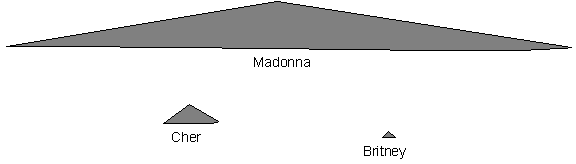
Refer to Figure 2 when answering
questions 23, 24 and 25.
Figure 2. Typical cross-sections showing the general shape and relative size
of different volcanoes.
24. In Figure 2,
A. A
shield volcano.
B.
A composite
volcano.
C. A
cinder cone.
D. An extinct volcano.
E.
A vocal volcano.
25. The volcano
labeled “Britney” in Figure 2 would be produced from what type of magma?
A.
High
viscosity
B. Low
viscosity
C. High
temperature
D. Low
temperature
E. Magma type can not be determined from the information given.
26. A volcano formed in the middle of an ocean basin would be most like which volcano in Figure 2?
A.
Madonna
B.
C. Britney
D.
None of the above, because a volcano formed in the
middle of an ocean basin would be most like J.Lo,
which is not shown in Figure 2.
27. What type
of volcano would likely form from a basaltic magma erupting on the ocean floor?
A. A shield volcano.
B.
A cinder cone.
C.
A composite volcano.
D.
A caldera volcano.
E.
An oceanic volcano.
28. 
What is the direction of longshore drift in the
diagram below?
A. From
bottom to top
B. From
top to bottom
C.
From left to
right
D. From
right to left
E.
The direction of longshore
drift cannot be determined from the diagram.
29. Which of
the following is the best definition of the Eckman
Layer?
A. The
average depth of water in the abyssal plane.
B. The
layer of water where plant life can flourish.
C. The
depth of sunlight penetration.
D. The
layer of water above the continental shelf.
E. None of the above is a definition of the Eckman Layer.
30. A wave has
a wavelength of 10 meters, how deep is the wave base?
A. 10
meters
B. 20
meters
C. 2
meters
D.
5 meters
E.
ocean depth at that spot
31. For a wave
occurring in the middle of the ocean, the motion of water particles is best
described as______.
A. Stationary.
B.
Circular
with no net movement.
C. Elliptical
with net movement forward.
D. Linear
push forward.
E.
None of the above.
32. Which of
the following does not occur as a wave approaches and crashes on the beach?
A.
Wave base
increases.
B. Wavelength
shortens.
C. Wave
height increases.
D. Wave
base touches bottom.
E.
Wave slows down.
33. Which of
the following is the main cause of deep ocean currents?
A. Winds.
B. Coriolis.
C.
Density
differences.
D. All
of the above.
E.
None of the above.